
注解
声明Bean注解
- @Component: 组件,没有明确规定其角色,作用在类级别上声明当前类为一个业务组件, 被 spring ioc 容器维护
- @Service:在业务逻辑层(Service 层)类级别进行声明,被 spring ioc 容器维护
- @Repository:在数据访问层(dao 层) 类级别进行声明,被 spring ioc 容器维护
- @Controller:标注当前类是一个控制器
注入Bean注解
在Set方法或属性上声明,推荐用 @Resource
- @Autowired
- @Inject
- @Resource
配置与获取Bean注解
- @Configuration:作用在类上,将当前类声明为一个配置类,相当于一个xml文件
- @ComponentScan:自动扫描指定包下标注有
@Repository @Service @Component @Controller 的类
- @Bean:作用于方法上,相当于 xml 文件中的 声明当前方法返回值为一个bean
- @Value:获取 properties 文件指定 key 的 value值
IOC中Bean的实例化与获取
创建项目
创建一个普通的Maven项目
引入spring核心依赖,修改jdk版本
pom.xml1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>shsxt-spring5</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>shsxt-spring5</name>
<url>http://www.example.com</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.18</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
</build>
</project>
|
创建Bean对象
dao 层
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| package org.example.dao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class UserDao {
public void test(){
System.out.println("userDao test...");
}
}
|
service 层
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| package org.example.service;
import org.example.dao.UserDao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserService {
private final UserDao userDao;
public UserService(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void test(){
this.userDao.test();
System.out.println("UserService test...");
}
}
|
创建IcoConfig配置类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| package org.example.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("org.example")
public class IocConfig {
}
|
创建启动类执行测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| package org.example;
import org.example.config.IocConfig;
import org.example.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Starter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(IocConfig.class);
UserService bean = applicationContext.getBean(UserService.class);
bean.test();
}
}
|
@Bean注解使用
使用 @Bean 注解声明在方法级别(方法名一般为bean对象的名称)用于返回实例化的 bean 对象。
Bean对象
注意:这个bean对象没有注解
目标Bean对象1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| package org.example.dao;
public class AccountDao {
public void test(){
System.out.println("AccountDao test...");
}
}
|
IocCofnig配置类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| package org.example.config;
import org.example.dao.AccountDao;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("org.example")
public class IocConfig {
@Bean
public AccountDao accountDao() {
return new AccountDao();
}
}
|
执行测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| package org.example;
import org.example.config.IocConfig;
import org.example.dao.AccountDao;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Starter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(IocConfig.class);
AccountDao bean = applicationContext.getBean(AccountDao.class);
bean.test();
IocConfig iocConfig = applicationContext.getBean(IocConfig.class);
AccountDao bean2 = iocConfig.accountDao();
bean2.test();
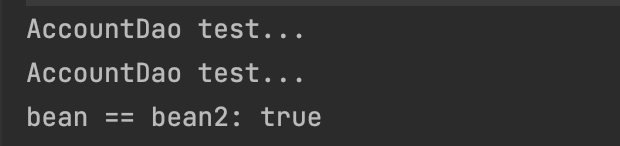
System.out.println("bean == bean2: " + (bean == bean2 ? "true":"false"));
}
}
|
运行结果
读取外部配置文件
对于配置文件的读取,我们可以通过 @PropertySource 注解声明到类级别来指定读取相关配置。
Spring El 表达式语言,支持在 xml 和注解中使用表达式,类似于 JSP 中 EL表达式,Spring 框架借助该表达式实现资源注入,主要通过 @Value 注解来使用表达式,通过 @Value 注解,可以实现普通字符串、表达式运算结果、Bean属性文件内容、属性文件等参数注入。
准备配置文件
src/main/resources 目录下添加 user.properties jdbc.properties 文件
user.properties1
2
| user.userName=admin
user.password=123456
|
jdbc.properties1
2
3
4
| jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/hr?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root
|
加载配置文件
通过 @PropertySource 注解加载配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| package org.example.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("org.example")
@PropertySource(value = {"classpath:user.properties", "classpath:jdbc.properties"})
public class IocConfig {
@Value("${user.userName}")
private String userName;
@Value("${user.password}")
private String userPassword;
public void showConfig(){
System.out.println(this.userName + " / " + this.userPassword);
}
}
|
测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| package org.example;
import org.example.config.IocConfig;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Starter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(IocConfig.class);
IocConfig iocConfig = applicationContext.getBean(IocConfig.class);
iocConfig.showConfig();
}
}
|
组合注解及元注解
自定义组合注解
整合 @Configuration 和 @ComponentScan 注解为一个自定义组合注解
自定义组合注解1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| package org.example.annoation;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Configuration
@ComponentScan
public @interface MyCompScan {
String[] value() default {};
}
|
组合注解使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| package org.example.config;
import org.example.annoation.MyCompScan;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
@MyCompScan("org.example")
@PropertySource(value = {"classpath:user.properties", "classpath:jdbc.properties"})
public class IocConfig {
@Value("${user.userName}")
private String userName;
@Value("${user.password}")
private String userPassword;
public void showConfig(){
System.out.println(this.userName + " / " + this.userPassword);
}
}
|


